Let’s admit it, A-Level / IAL Chemistry is hard. Not only hard but super hard. It is much tougher than IGCSE Chemistry. If you want to survive in the IAL chemistry exam, you definitely need some good help. A few easy marks in the bag would help you to survive or even do good in the exams.
What most people do not realize is that many questions are repeated in the IAL chemistry exams. Either the values are changed or the conditions or scenarios are changed up a little bit. But more or less they are the same. In this blog, I am going to list down many common questions which come in IAL chemistry UNIT-1 Exam! Along with proper answers too!
Below is the table of contents for the question/answers. I have divided the questions into several topics. So it is easier for you to navigate, so you can quickly get the question-answers that you are looking for. Just scroll through the question answers, you will most probably find the ones you need.
Reminder: you can get the extended version of these common questions Edexcel IAL Chemistry Unit 1 Common Questions and Answers: Study and Revision Guide from Amazon in kindle or paperback formats

Revise IAL Chemistry unit 1 within 1 hour & get above 90%
- No BS, to the point, quick, and easy to revise.
- Actual common questions with answers from the question paper. Get easy marks in the bag during your exam.
- Questions are divided into different topics.
- A brief discussion on each topic to get your concepts clear.
- Available in kindle ebook and paperback formats on Amazon
Random Short Question/Answers
1) Define the first ionization energy.
Answer: The enthalpy change when one electron is removed from one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of +1 charged ions.
2) Define covalent bonds.
Answer: Electrostatic attraction between the two nuclei and the bond pair electrons.
3) Define the term Relative Atomic Mass.
Answer: Average masses of all the isotopes of an element, the mass of each isotope is found by comparing with the carbon-12 isotope.
4) Explain the term structural isomers.
Answer: Compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
5) Define the term Lattice Enthalpy.
Answer: The enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from gaseous ions.
6) Define the term enthalpy change of reaction.
Answer: Enthalpy change when the number of moles of reactants reacts as specified in the balanced equation.
7) What is meant by the term mean bond enthalpy?
Answer: Average amount of energy required to break one mole of covalent bonds.
8) State in terms of the sub-atomic particles present, the meaning of the term isotopes.
Answer: Atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
9) Define the term standard enthalpy change of formation of a compound.
Answer: Enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its element under standard conditions of 298K and 1 atm pressure.
10) State what is meant by the term unsaturated as applied to a hydrocarbon.
Answer: contains carbon to carbon double bond.
11) State what is meant by the term cracking when applied to processing a reaction obtained from crude oil.
Answer: Breaking down large hydrocarbons to smaller hydrocarbons
12) Define the term relative isotopic mass.
Answer: Mass of an isotope of an element relative to 1/12th the mass of a 12C isotope.
13) State Hess’s law.
Answer: The enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the route of the reaction.
14) Define the term standard enthalpy change of formation, making clear the meaning of standard in this context
Answer: Enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements unde4 standard conditions of 298k and 1 atm pressure.
15) On the basis of comparing the relative sizes of fluorine and chlorine atoms, it might be predicted that the F-F bond energy would be greater than the Cl-Cl bond energy. Suggest an explanation for this prediction.
Answer: Fluorine atom is smaller than a Cl atom, bond pair closer to the nuclei
16) Which element on the periodic table has the highest first ionization energy? Justify your answer.
Answer: Helium, no shielding
17) State how you could find the molecular mass of a substance from a mass spectrometer.
Answer: peak with the largest mass
18) Explain why the melting temperature of argon is the lowest of all the elements of period 3
Answer: Argon contains only monoatomic atoms

Answer: Find out the abundance of the 14C in the cloth, use the half-life of 14C to find the age of cloth.
19) State and explain the main environmental problem arising from the complete combustion of alkane fuels.
Answer: Global warming
Important: I have divided the following common questions below based on their topics. Before you progress your concepts must be crystal clear.
Reminder: you can get the extended version of these common questions Edexcel IAL Chemistry Unit 1 Common Questions and Answers: Study and Revision Guide from Amazon in kindle or paperback formats
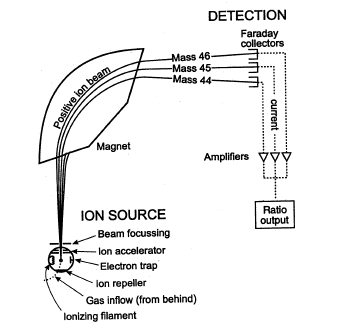
Mass Spectrometer
In the mass spectrometer, the gaseous atoms are ionized by bombardment with high-energy electrons, accelerated by the electric field, positive ions are deflected by a magnetic field.
Common Question/Answers
Describe briefly how positive ions are formed from gaseous atoms in a mass spectrometer
Answer: By bombarding with high energy electron
What is used to accelerate the positive ions in a mass spectrometer?
Answer: Electric field
What is used to deflect positive ions in a mass spectrometer
Answer: Magnetic field
Explain how gaseous atoms of rubidium are ionized in a mass spectrometer.
Answer: Bombardment with electrons
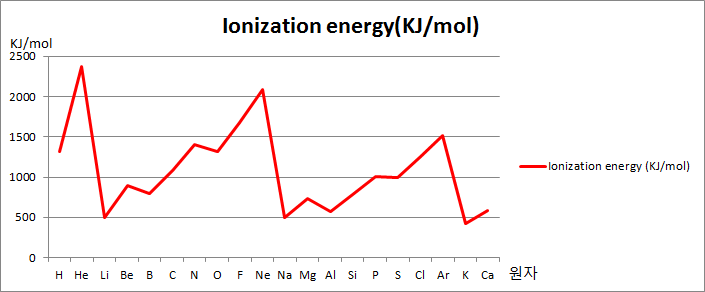
First Ionization Energy across a period
The first ionization energy increases across a period, the number of protons increases but the number of shells remains the same, shielding remains the same, so outer shell electron feels greater nuclear attraction.
Note: Please keep a periodic table beside you while studying this, the question may be asked in different ways using different elements across different periods but the answer remains the same.
Common Question/Answers
Explain why the first ionization energies generally increase across the period Sodium to argon (Na to Ar)?
Answer: Across the period the proton number increases but shielding remains the same as the number of shells remains the same, so greater attraction between the nucleus and outer electrons.
Explain why there is a general increase in the first ionization energies from sodium to argon
Answer: Across the period proton number increases while shielding remains the same as a number of shells remains the same, greater attraction between the nucleus and outermost electrons.
Explain why the first ionization energy of krypton is higher than that of selenium?
Answer: The number of protons increases while shielding remains the same due to the same number of shells, greater nuclear attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
Explain why, in moving from Na to Ar, the general trend is for the first ionization energy is to increase?
Answer: The number of protons increases while shielding remains the same due to the same number of shells, greater nuclear attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
Reminder: you can get the extended version of these common questions Edexcel IAL Chemistry Unit 1 Common Questions and Answers: Study and Revision Guide from Amazon in kindle or paperback formats
First Ionization Energy down the group
The first ionization energy decreases down the group, though the number of protons increases down the group, shell number increases, shielding increases, outer electrons are further away from the nucleus, they feel less attracted to the nucleus.
Note: The questions can be asked in different styles or manners, but the answers remain the same. Please have a look at these questions from the question paper. Please keep a periodic table while revising these questions.
Note: Please keep a periodic table beside you while studying this, the question may be asked in different ways using different elements across different periods but the answer remains the same.
Common Question/Answers
Explain why the first ionization energy of rubidium is lower than that of krypton (2 marks)
Answer: Down the group number of shells increases, the outer electrons are further away from the nucleus, more shielding, the outer shell electron feels less attraction towards the nucleus.
Explain why the first ionization energy of the elements down Group 1 decreases even though the atomic number increases.
Answer: Down the group number of shells increases, the outer electrons are further away from the nucleus, more shielding, the outer shell electron feels less attraction towards the nucleus.
Suggest why the first ionization energies of group1 elements decrease down the group.
Answer: Down the group number of shells increases, the outer electrons are further away from the nucleus, more shielding, the outer shell electron feels less attraction towards the nucleus.

Revise IAL Chemistry unit 1 within 1 hour & get above 90%
- No BS, to the point, quick, and easy to revise.
- Actual common questions with answers from the question paper. Get easy marks in the bag during your exam.
- Questions are divided into different topics.
- A brief discussion on each topic to get your concepts clear.
- Available in kindle ebook and paperback formats on Amazon
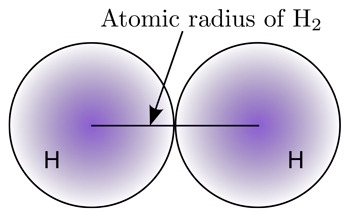
Atomic radius across the period
Atomic radius across the period: The atomic radius decreases across the period, because across the period proton number increases, but the number of shells remains the same, shielding remains the same, hence outer shell electrons feel higher attraction towards the nucleus.
Note: Questions may use different periods and different elements.
Common Question/Answers
Suggest why the atomic radius decreases going across the period from sodium to argon.
Answer: Across the period proton number increases, but the number of shells remains the same, shielding remains the same, hence outer shell electrons feel higher attraction towards the nucleus.
Which of the elements Arsenic to Rubidium, is likely to have atoms with the smallest atomic radius.
Answer: Krypton
Successive ionization energies
Successive ionization energies mean one ionization after the other, for example, the first ionization energy, second ionization energy, and third ionization energy, and so on.
Note: The asking style may be different, but the answer is the same.
Note: Questions may use different periods and different elements.
Common Questions/Answers:
Give two reasons why the second ionization energy of magnesium is greater than the first ionization energy of magnesium.
Answer: Electron is being removed from a positive ion, the greater force of attraction between the nucleus and outermost electron.
Explain why the successive ionization energies increase
Answer: Electron is being removed from a positive ion, the greater force of attraction between the nucleus and outermost electron.
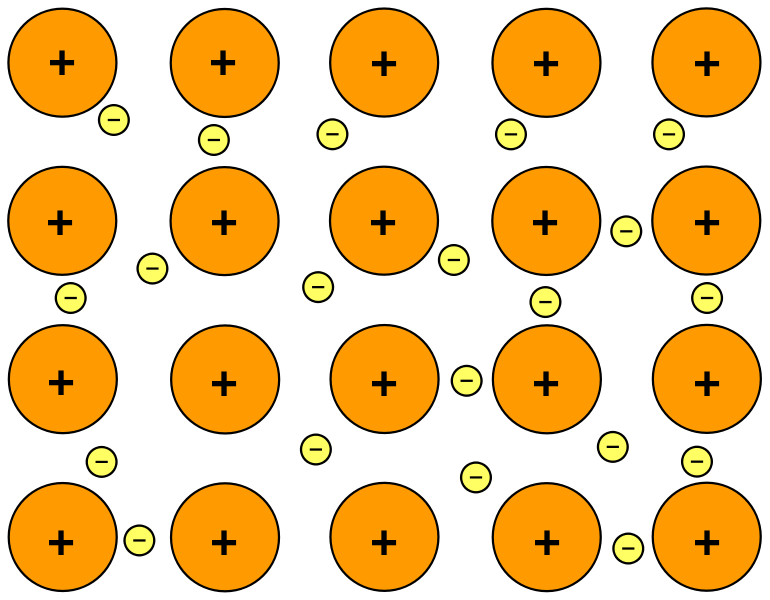
Structure of metal
Common Question/Answers
Describe the structure of a metal
Answer: Closely packed lattice, positive ions surrounded by delocalized electrons
Note: this question also can be asked by naming a metal, for example, describe the structure of sodium
Describe the bonding in a metal
Answer: Electrostatic attraction between cations and delocalized electrons.
Note: this question also can be asked by naming a metal, for example, describe the bonding in sodium
Explain how metals conduct electricity
Answer: The delocalized electrons flow when voltage is applied.
Metals structure that contains high charged cations has high melting points. These are the following questions which may be asked, answer them properly to obtain full marks.
Common Question/Answers
Explain fully why the melting temperature of magnesium is higher than that of sodium. (3 marks)
Answer: Mg2+ has a larger charge than Na+, Mg2+ is smaller than Na+ ion, therefore more energy is required to overcome the attractive forces between cations and sea of delocalized electrons.
Explain why the melting temperature increases from sodium to aluminum.
Answer: Charge of cation increases, the force of attraction between cations and delocalized electrons increases.
Metals are good conductors of electricity while simple molecular substances are bad conductors of electricity:
Common Question/Answers
Explain why magnesium is a good conductor of electricity whereas sulfur is a non-conductor.
Answer: Magnesium has delocalized electrons whereas sulfur’s electrons are fixed in a covalent bond
Giant Covalent Structure
Giant Covalent Structure has greater melting point than simple molecular structure
Common Question/Answers
Explain the following referring to differences in structure and bonding Silicon has a higher melting temperature than phosphorous.
Answer: Silicon is a giant covalent structure while phosphorous is simple molecular, strong covalent bonds throughout the whole structure but weak intermolecular forces in phosphorous which takes lower energy to overcome.
Explain why silicon has a much higher melting temperature than sulfur.
Answer: Silicon is a giant covalent structure while sulfur is simple molecular, strong covalent bonds throughout the whole structure but weak intermolecular forces in sulfur which takes lower energy to overcome.
Giant covalent structures have high melting points: Examples of giant covalent structures are diamond, graphite, silicon dioxide, and silicon, no matter which one you are asked about, the explanation is going to be the same.
Common Question/Answers
Explain the high melting temperature of silicon in terms of the bonding.
Answer: Silicon is a giant covalent structure, strong covalent bonds throughout the whole structure, which takes a lot of energy to break.
Giant covalent structures such as diamond, silicon dioxide, and silicon have low electrical conductivity, please note graphite is not among them as graphite is a good conductor of electricity:
The electrical conductivity of pure silicon is very low. Explain why this is so in terms of the bonding.
Answer: Silicon’s outer electrons are fixed in a covalent bond, therefore silicon’s electrons are not free to move.
Note: same explanation can be used for diamond and silicon dioxide.
Incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon
Identify two other products that could form if the combustion was incomplete.
Answer: soot/carbon/C, Carbon Monoxide (CO)
State two problems that result from the incomplete combustion of alkane fuels.
Answer: poisonous CO formed, unburned hydrocarbons are toxic
Why alkenes are more reactive than alkanes
Common Question/Answers
By considering the strength and structure of the 𝝅-bond, explain why alkanes are more reactive than the alkanes.
Answer: 𝝅-bond is weaker than the σ-bond, because of higher electron density in the 𝝅-bond, so alkenes are more susceptible to attack by electrophiles.

Revise IAL Chemistry unit 1 within 1 hour & get above 90%
- No BS, to the point, quick, and easy to revise.
- Actual common questions with answers from the question paper. Get easy marks in the bag during your exam.
- Questions are divided into different topics.
- A brief discussion on each topic to get your concepts clear.
- Available in kindle ebook and paperback formats on Amazon
How electron affinities changes down the group
State and explain how electron affinity values change as you go down group 7 from chlorine to iodine.
Answer: Electron affinities become less negative as an added electron is further away from the nucleus
Crystallization Method
How to do crystallization method to obtain pure dry crystals from a salt solution
Common Question/Answers
State and explain the steps necessary to obtain pure dry crystals from the mixture (from a salt solution) (4 marks)
Answer: Heat the solution of remove water, cool to let crystals form, separate crystals using filtration method, dry crystals using filter paper.

Answer: Add MgO to acid, heat to remove water, filter, leave to cool, filter to remove crystals, leave crystals to dry.
Covalent Bond
How atoms are held together in a covalent bond: The nuclei of the two atoms are attracted towards the shared electron pair.
Note: the question may be asked in different ways, but the answer is the same.
Common Question/Answers
Explain how the atoms are held together by the covalent bond in a molecule of hydrogen
Answer: Electrostatic attraction between the bond pair electrons and nuclei
Isotopes
Isotopes have similar chemical properties: because they have the same electronic configuration.
Common Question/Answers
Explain why four isotopes of chromium behave identically in chemical reactions
Answer: Same electronic structure or configuration
Type of force in ionic lattice
Common Question/Answers
Describe the forces of attraction in an ionic lattice
Answer: Forces of attraction between oppositely charged ion
Suggest two forces of repulsion that exist in an ionic lattice
Answer: Between ions of the same charge, nuclei of ions
Difference between hazard and risk
Common Question/Answers
Explain the difference between hazard and risk.
Answer: Hazard means a substance that has the potential to do harm, whereas risk means the chance of causing harm.
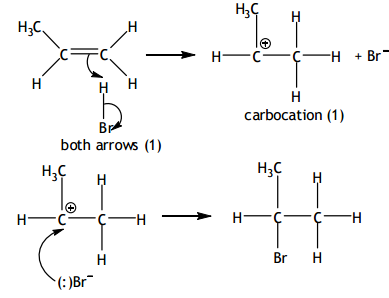
Free radical substitution

Mechanism for the reaction between propene and hydrogen bromide
Give the mechanisms for the reaction of propene with hydrogen bromide (HBr) to form the major product.
Lattice Enthalpy
The lattice enthalpy for an ionic compound becomes more negative or exothermic if the ions are smaller, or the ions have a higher charge.
Common Question/Answers
Explain, in terms of sizes and charges of the ions involved, why the lattice energy of MgF2 is more negative than the NaF
Answer: Mg2+ is smaller than Na+, Mg2+ has a higher charge than Na+, so greater attraction between MgF2 and NaF so more energy released.
Explain, in terms of the size and charges of the ions involved, the differences between the lattice energy values of:
i) NaF and NaCl
Answer: NaF is more negative than NaCl because F- is smaller than Cl-, so higher attraction with Na+, hence releases more energy.
ii) NaF and MgF2
Answer: MgF2 is more negative/exothermic because Mg2+ is smaller than the Na+ ion, also Mg2+ has a greater charge than Na+, so higher attraction and more energy are released.
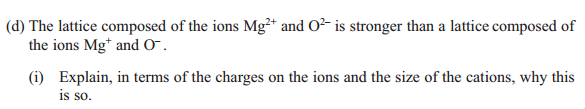
Answer: Mg2+ and O2- have higher charges, Mg2+ is smaller, and therefore lattice energy of Mg2+ and O2- is more exothermic
Theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpy
The theoretical lattice enthalpy is the one that is found by coulombs law, and the experimental lattice enthalpy is which is found from the born-Haber cycle. The experimental lattice enthalpy is always more exothermic than the theoretical lattice enthalpy because in theory it is assumed that no polarization occurs/ distortion of anion by the cation, but in actual polarization does occur. Polarization gives rise to covalent character, meaning higher attraction leading to more energy released. A smaller and higher charged cation means it has more polarizing power, the higher charged anion, and big means that it is more polarizable. The more the polarization the more exothermic the experimental lattice enthalpy than the theoretical lattice enthalpy. If little or no polarization then the theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpy would be very close.
Common Question/Answers
Lattice energies can be calculated from electrostatic theory (theoretical values) as well as Born-Haber cycles (experimental values)
What can you deduce from the fact that the experimental and theoretical calues for the lattice energy of barium chloride are very close?
Answer: Bonding is 100% ionic/no covalent character/chloride ions not polarized
The experimental lattice energy for lithium iodide is -759 KJmol-1. The theoretical lattice energy is different from this value, will the experimental lattice energy be more negative than the theoretical lattice energy? Justify your answer.
Answer: Experimental lattice enthalpy is more negative, due to the degree of covalence, because of the polarization of iodide ions.
Explain why there is a greater difference between the experimental (Born-Haber cycle) and theoretical lattice energies for Magnesium Iodide, MgI2 compared with magnesium chloride.
Answer: I- is larger than Cl-, easier to polarize
Explain, in terms of chemical bonding, why the experimental value for silver iodide, AgI is more exothermic than the value calculated theoretically for the same compound.
Answer: AgI has a degree of covalent character, due to the polarization of the anion
Ionic compound melting point
An ionic compound will have a higher melting point if it consists of ions with higher charges, then there would be a greater attraction between the ions, and would require more energy to overcome.
Common Question/Answers
Suggest why the melting temperature of magnesium oxide is higher than that of magnesium chloride, even though both are almost 100% ionic.
Answer: O2- ions have a higher charge than Cl-, the force of attraction is greater in MgO, and more energy is required to separate the ions in MgO.
Yield of salt preparation
The crystals of a salt being produced always have a yield of less than 100%.
Common Question/Answers
Give one reason why the yield of crystals is less than 100%, even when pure compounds are used in the preparation.
Answers: Transfer losses, crystals left behind, loss on filtering
Finding enthalpy change
Finding enthalpy change of alcohol by cup calorimetry method :
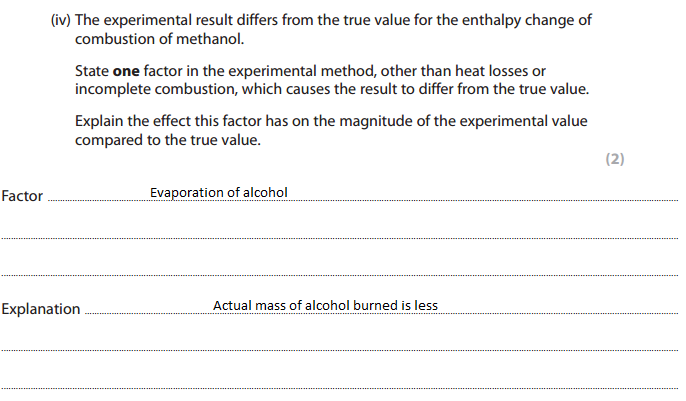
List three ways in which the design of the experiment causes the results to be so different from the databook value.
Answer: Heat loss, incomplete combustion of alcohol, evaporation of alcohol
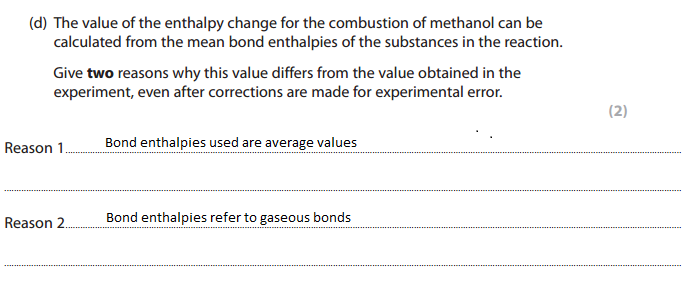
Finding the enthalpy change of combustion using mean bond enthalpy is inaccurate:

Revise IAL Chemistry unit 1 within 1 hour & get above 90%
- No BS, to the point, quick, and easy to revise.
- Actual common questions with answers from the question paper. Get easy marks in the bag during your exam.
- Questions are divided into different topics.
- A brief discussion on each topic to get your concepts clear.
- Available in kindle ebook and paperback formats on Amazon
Ionization energy comparison
The first ionization energies generally increase from left to right across the period
Common Question/Answers
i) Explain why the first ionization energy of sulfur is lower than that of phosphorous
Answer: There are two electrons in the same (3p) orbital, repulsion allows electrons to be removed easily.
ii) Explain why the first ionization energy of nitrogen is greater than the first ionization energies of phosphorous
Answer: The outer shell electrons are in a shell closer to the nucleus in N, less shielding, greater attraction between the nucleus and the outer electron.
Explain why the first ionization energy of selenium is lower than that of arsenic.
Answer: In Se electron removed from orbital containing two electrons, increase n repulsion so electron lost more easily.
Explain why the first ionization energy decreases from P to S
Answer: Two electrons occupy the same orbital, repulsion between paired electrons
Explain why the first ionization energy of Aluminium (z=13) is less than that of Magnesium (z=12)
Answer: Electron lost from 3p subshell in Al, which is at higher energy further from the nucleus
Explain why the first ionization energy of sulfur (z=16) is less than that of phosphorous (z=15)
Answer: Electron lost from a pair of electrons, increase in repulsion, electron lost more easily.


Thank you very much, sir!
Sir, can you also make the same Unit 1.
Please please please!
Sorry, I meant can you also make the same for Unit 2 and unit 3?
Please please please!
Sure man, already working on Unit-2.
YES THANKYOU! Pls let us know when ur done with unit 2 and 3!
I am already working on Unit 2, will be done soon!
thank you so much for your hardwork
Hi!
Do you have a pdf version of this? My exam is next Tuesday and would really appreciate it.
Thank you so much Sir this is a great resource for some last minute revision!
Most welcome dear 🙂
may i get the full notes for EDEXCEL IAL chemistry please?
thanks in advance
hii could you make this for unit 4 as well. you’re literally a lifesaver oml i owe u fr
hii could you make this for unit 4 as well. you’re literally a lifesaver oml i owe u fr
Hey man thank you so much is there one on unit 4?
Sorry dear, not yet 🙁
hey, thank you . do u have unit these for unit 3?