Halogenoalkanes
Halogenoalkanes are a homologous series in the organic chemistry. They are compounds with alkyl radicals with halogen atom or even atoms as their functional group. There are three types of halogenoalkaes, they are primary, secondary and tertiary halogenoalkanes.
Example: R-Cl , R-Br , R-F
To review your basics with organic chemistry, please click here
- Halogenoalkanes are used in medicines, agriculture and production of plastics
- The halogenoalkanes may also have multiple halogen atoms attached to the alkyl group
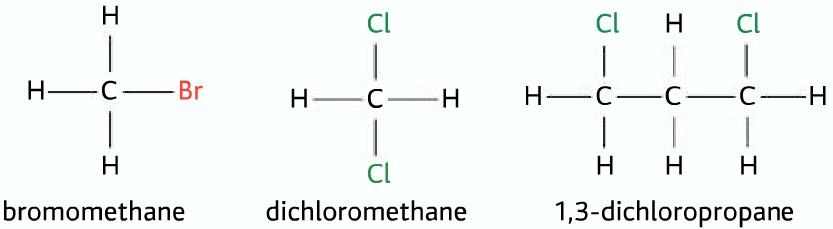
The property of halogenoalkane depends on three factors:
- The type of hydrocarbon skeleton (short or long)
- The halogen or halogens attached (what halogens and how many)
- The position where halogen is attached(primary, secondary or tertiary)
Halogenoalkanes can also be primary , secondary or tertiary
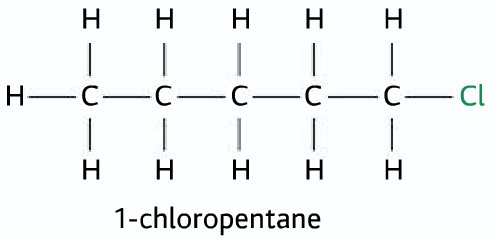
Primary Halogenoalkane
one alkyl group and two hydrogen atom connected to the carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached.
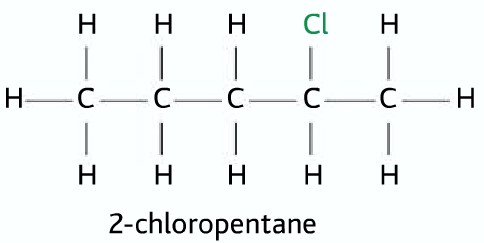
Secondary halogenoalkane
Two alkyl groups and one hydrogen atom attached to the carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached.
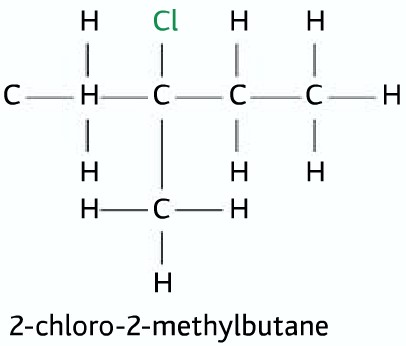
Tertiary Halogenoalkanes
Three alkyl groups and no hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atom to which the halogen atom is attached.
Uses of halogenoalkanes
- Halogenoalkanes can be used as anesthetics
- Halogenoalkanes are used as refrigerants:
Refrigerant Are fluids which circulate inside the freezers and air conditioners, turning from gas to liquid and vice versa.
Characteristics of a good refrigerant
- Changes from gas to liquid and back at a temperature below the temperature of the refrigerators.
- High enthalpy of vaporization, has a moderate density in liquid form and high density in vapor form.
- Not toxic, flammable or corrosive.
In early times NH3 , SO2 were used as refrigerants, but they are poisonous.
CFC(Chlorofluorocarbons) : This type of halogenoalkane is used as refrigerants. It contains both C-F and C-Cl bonds, based on methane and ethane.
A special type of naming system is used to name the refrigerants. Here are the rules of what the code means.
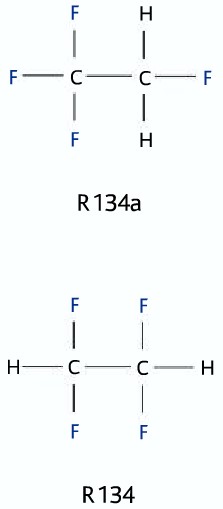
Rightmost Digit: Number of fluorine atoms per molecule
Tens digit: One plus the number of hydrogen atoms per molecule
Hundreds digit: number of carbon atoms minus one
Thousands digit: Number of double bonds in the molecule (this is omitted when zero)
A suffix of lower case letter a,b,c indicates unbalanced isomers.
Problems with CFC
- Ozone (O3) gas is formed in the upper part of the atmosphere. It absorbs harmful UV rays and protects everyone from skin cancer.
- CFC does not break down in the lower part of the atmosphere. But when goes to the top part, UV rays act on it and it undergoes hemolytic fission and produces free radicals.
- The highly reactive chlorine free radicals then attack the ozone (O3) molecules.
Cl• + O3 → ClO• + O2
ClO• + O3 → Cl• + 2O2
Net Reaction: 2O3 → 3O2
Note: Chlorine free radical (Cl•) is not used up. So one chlorine free radical can destroy thousands of ozone molecules.
Effects: Ozone concentration decreases, a hole may be created, allowing more UV rays to enter, increasing the chances of skin cancer.
Alternatives to CFC:
- One alternative to CFC is HCFC (Hydro Chloro Fluro Carbon). It also contains C-F and C-Cl bonds, but it breaks down in the lower part of the atmosphere. So it doesn’t deplete the ozone layer. But HCFC is a greenhouse gas.
- Another alternative is HFC (Hydro Fluro Carbon) it contains strong C-F bonds and no C-Cl bonds. The C-F bond doesn’t break.
- Butane is also an alternative to CFC but it is flammable.
Halogenoalkanes can be used as fire retardants because:
- They have a low boiling point of 4° C, vaporizes when sprayed.
- Does not burn in oxygen
- Heavier than air so falls and covers the fire.
Problems with halogenoalkane fire retardants:
- Causes depletion of ozone layer.
- Have narcotic effects
How to make fire retardant fabric
- Finishing the fabric with flame retardant chemicals
- Adding flame retardant to the polymer, before it is made into fiber.
- Using polymer containing chlorine, bromine or fluorine

